Big data is a term used to describe massive amounts of structured and unstructured data. These data are generated by individuals, organizations, and digital devices. In this topic, we will explore the different types of big data, their applications across various industries, and the 5Vs of big data – volume, velocity, variety, veracity, and value – that make it unique and challenging to manage and analyze.
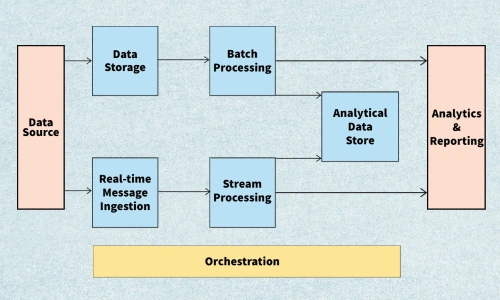
Big Data Architecture
What is Big Data Analytics?
Big data refers to extremely large and complex datasets that are too difficult to manage and analyze using traditional data processing methods. It involves gathering, storing, and analyzing vast amounts of information from various sources such as social media, sensors, and other digital devices.
KEY TAKEAWAYS
- The size of big data can range from thousands of gigabytes (terabytes) to millions of gigabytes (petabytes) or even more.
- Big data is analyzed using advanced technologies such as machine learning and artificial intelligence.
- It is a branch of AI that is analyzed computationally to reveal patterns, insights, trends, and human behavior.
- Big data is transforming industries such as healthcare, finance, and transportation by enabling more informed decisions and improving outcomes.
- Big data is mainly characterized by the 3 V’s: Volume, Velocity, and Variety.
Types of Big Data
Big data is often classified into different types based on its structure and level of organization. The three primary types of big data are structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data. Now, we’ll discuss each type to understand what they mean.
- Structured Data: This type of data is organized and can be easily categorized into specific fields or columns, such as in a spreadsheet. Structured data is usually generated by machines and is the most straightforward type of data to work with.
Example: Date, Phone number, and Customer name. - Semi-structured Data: This type of data is not organized in a specific format like structured data, but it still contains some organizational elements such as tags or labels that allow it to be grouped and sorted. Semi-structured data is commonly found in emails, social media posts, and XML files.
Example: Tweets organized by hashtags, Email sorting by folder(inbox, sent, draft). - Unstructured Data: This type of data is not organized in any specific way and doesn’t have any labels or structure. Examples of unstructured data are emails, images, videos, and audio files. Dealing with unstructured data is really hard but it also has the greatest potential for generating meaningful insights.
Now, it’s time to understand the important Vs of big data which is the main factor of big data analytics.
5Vs of Big Data
Data professionals use the “5Vs of Big Data” framework to make sense of this massive amount of information. This framework describes the five key characteristics that define Big Data and enables data experts to make sense of the data.
- Volume: This refers to a very large or huge amount of data. It includes unvalued data such as Twitter data feeds, clickstreams on a web page or mobile app, or sensor-enabled equipment. This could amount to thousands of terabytes of data for some organizations. Others may require hundreds of petabytes.
- Velocity: It refers to the speed or flow of data. It is the speed at which data is generated, received, and processed. Real-time data processing has become essential for businesses to remain competitive.
- Variety: Variety refers to the different formats of data from various sources. The format may vary from structured numeric data to unstructured and semi-structured data types, such as text, audio, and video.
- Veracity: It refers to the quality, accuracy, and reliability of the data. Because the data comes from multiple sources, it is nearly difficult to link, match, sort, and transform data across systems.
- Value: This means the potential benefits that can be gained from analyzing and utilizing the data. By extracting insights and trends from Big Data, businesses can make informed decisions, improve operations, and gain a competitive advantage.
After understanding the 5Vs of big data, let’s move ahead to some areas where big data is generally applied.
Applications of Big Data
Big data is an essential tool for organizations of all sizes to gain insights, make informed decisions, and improve operations. This includes:
- Astronomy
- Healthcare
- Education
- E-commerce
- Finance
- Entertainment
- Transport
- Social Media
These are the numerous applications of big data across various industries. Now, quickly come to some advantages and disadvantages of the b-data.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of big data?
Organizations must also be aware of the advantages and potential drawbacks of big data and take steps to mitigate them.
Advantages
- Products and services are better personalized to meet the need of users.
- Errors inside the business are known immediately.
- Identify inefficiencies and reduce future costs.
- Improve decision-making to boost operations and competitiveness.
Disadvantages
- The quality of the data can impact accuracy and reliability.
- Expensive and requires significant investments in technology.
- Inaccurate data leads to more noise and errors.
- Security is a major concern because of the huge amount of data collection.
Conclusion
In conclusion, big data is emerging as a game-changer for organizations in various industries, providing valuable insights growth, and innovation. It is an important factor for large industries to achieve their business goals in a data-driven world. The different types of big data offer unique challenges and opportunities for understanding trends and analytics.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q. What are the 4 benefits of big data?
Ans. Cost-saving, Time-saving, Customer acquisition, and Innovation are the four major benefits of big data.
Q. What are the 5 sources of big data?
Ans. The main five sources/drivers of big data are Social media, Mobile applications, Medical records, Customer databases, and Internet search intent.
Q. What are the 3 main Vs of big data?
Ans. The three primary Vs of big data include Volume, Velocity, and Variety.

Ankit Roy is a professional Technical Content Developer, Freelancer, and blogger. He holds a Masters’s degree in Computer Science and has worked as a Digital Marketing Strategist. With a deep understanding of technology trends like AI, ML, Big Data, Neural Networks, Network Infrastructure, etc., Ankit is able to communicate complex technical concepts in a clear and concise manner. He is a regular contributor to several websites and has authored numerous technical guides and instructional materials. In his free time, Ankit enjoys tinkering with new technologies and staying up-to-date with the latest developments in the field.




